Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort.
In the most advanced cases, this inflammation can lead to new bone formation on the spine, causing the spine to fuse in a fixed, immobile position, sometimes creating a forward-stooped posture. This forward curvature of the spine is called kyphosis.
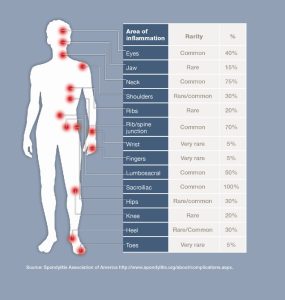
AS can also cause inflammation, pain and stiffness in other areas of the body such as the shoulders, hips, ribs, heels and small joints of the hands and feet. Sometimes the eyes can become involved (known as Iritis or Uveitis), and rarely, the lungs and heart can be affected.
The hallmark feature of ankylosing spondylitis is the involvement of the sacroiliac (SI) joints during the progression of the disease, which are the joints at the base of the spine, where the spine joins the pelvis.